Table of Contents:
-
Why Choosing A Rechargeable Generator Over A Traditional Generator?
-
POWEREPUBLIC Solar Generator Kits As Rechargeable Generators
With sustainability emerging as a worldwide concern and progressively influencing our daily lives, individuals are increasingly seeking eco-friendly and reusable energy solutions. This is why rechargeable generators are garnering growing interest.
In this article, we will delve into the concept of rechargeable generators, their various types, their practical applications, and their advantages in contrast to traditional generators, and introduce POWEREPUBLIC solar generator kits as one of the rechargeable generator options available.
What is a Rechargeable Generator?

In essence, a rechargeable generator serves as a dependable backup power source, enabling you to charge your devices and appliances during power outages or when the primary power supply is unavailable. This versatile device finds practical use in a variety of scenarios, such as providing power to remote areas, serving as an emergency backup, or meeting the energy needs of off-grid applications.
Also, it can be recharged using different energy sources, including solar and wind energy, making it a sustainable and adaptable solution for diverse power requirements.
What Are Some Common Types of Rechargeable Generators, and How Does Each Type Operate?

There are different types of rechargeable generators, such as solar generators, wind generators, and Hybrid generators. We will explain what are they and how they operate.
1. Solar Generators
Solar generators rely on photovoltaic panels (solar panels) to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity through the photovoltaic effect, making them a sustainable and renewable energy solution.
Key Components and Functions:
-
Solar Panels: Capture sunlight and convert it into DC electricity.
-
Charge Controller: Regulates the charging of the rechargeable battery.
-
Inverter: Converts DC electricity into AC for household use.
-
Rechargeable Battery (typically lithium-ion): Stores electricity for later use.
Energy Storage:
Electricity generated from solar panels is stored in the rechargeable battery.
Charging:
Solar panels produce DC electricity, managed by a charge controller to efficiently charge the battery.
Recharging:
Solar generators continue to recharge when exposed to sunlight, ensuring stored energy availability.
2. Wind Generators
Wind generators utilize wind turbines to capture the kinetic energy of the wind and convert it into electrical power, offering another renewable energy option.
Key Components and Functions:
-
Wind Turbine: Converts wind energy into mechanical energy, which is further transformed into electricity.
-
Charge Controller: Regulates battery charging from the generated electricity.
-
Inverter: Converts generated electricity (typically AC) into usable AC power.
-
Rechargeable Battery (typically lithium-ion or lead-acid): Stores electrical energy.
Energy Storage:
Electricity generated from wind turbines is stored in rechargeable batteries.
Charging:
Wind generators produce AC electricity, which is directed to a charge controller to charge the battery.
Recharging:
Wind generators continue to recharge when wind is sufficient, maintaining stored energy levels.
3. Fuel-powered Generators with Battery Storage
These generators combine traditional internal combustion engines with rechargeable batteries to provide reliable and versatile power solutions.
Key Components and Functions:
-
Internal Combustion Engine: Generates electricity and powers the system.
-
Generator: Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
-
Inverter: Converts generated AC electricity into usable AC power.
-
Rechargeable Battery (typically lithium-ion): Stores excess generated electricity.
Energy Storage:
Excess electricity produced by the internal combustion engine is stored in rechargeable batteries.
Charging:
The generator produces AC electricity, which is used for immediate needs and to charge the internal battery.
Recharging:
The battery recharges during generator operation, and it can be refueled to provide continuous power.
4. Hybrid Generators
Hybrid generators integrate multiple energy sources, such as solar panels, wind turbines, and backup fuel generators, to ensure a continuous and adaptable power supply.
Key Components and Functions:
-
Solar Panels: Capture solar energy for electricity generation.
-
Wind Turbine: Converts wind energy into electrical power.
-
Backup Generator (typically fueled by gasoline, diesel, or propane): Provides energy when renewable sources are insufficient.
-
Charge Controller: Manages battery charging from solar and wind sources.
-
Inverter: Converts generated electricity (DC or AC) into usable AC power.
-
Rechargeable Battery (typically lithium-ion): Stores excess energy.
Energy Storage:
Energy from solar panels and wind turbines is stored in rechargeable batteries, often using lithium-ion technology.
Charging:
Solar panels and wind turbines produce DC electricity, which is regulated by a charge controller to efficiently charge the battery. The backup generator runs when renewable energy is insufficient.
Charging:
The battery continuously recharges from renewable sources and the backup generator, ensuring an uninterrupted power supply.
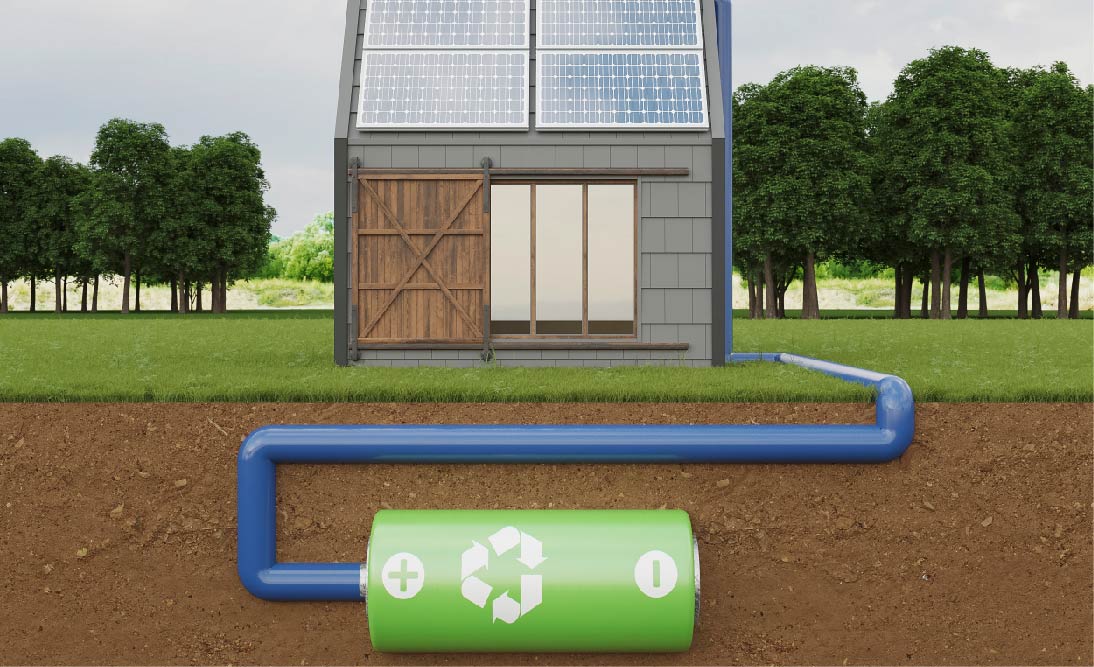
5. Home Energy Storage Systems
These systems are designed for residential use and store electricity from the grid or renewable sources in rechargeable batteries, promoting energy efficiency.
Key Components and Functions:
-
Rechargeable Battery (typically lithium-ion): Stores electrical energy for later use.
-
Inverter: Converts stored DC electricity into usable AC power.
-
Charge Controller: Manages the battery charging process.
-
Grid Interface: Facilitates recharging from the grid when necessary.
Energy Storage:
Electricity is stored in a rechargeable battery, reducing dependence on the grid and optimizing energy utilization.
Charging:
These systems charge during off-peak hours or when excess electricity is available, such as during periods of surplus power or from connected solar panels.
Recharging:
The battery can be recharged from the grid when power is available or from solar panels generating excess energy, ensuring a continuous and reliable energy supply.
Each type of rechargeable generator stores energy in a rechargeable battery or energy storage system charges through its specific power source, and recharges when that power source is active or when connected to other power sources, such as the grid or additional renewable energy systems. The goal is to ensure a continuous and reliable power supply by using stored energy when the primary power source is unavailable or insufficient.
In What Scenarios Can Rechargeable Generators Be Utilized?

Solar Generators
-
Residential Backup Power: Solar generators are used as backup power sources for homes during grid outages, ensuring essential appliances like refrigerators and lights continue to operate.
-
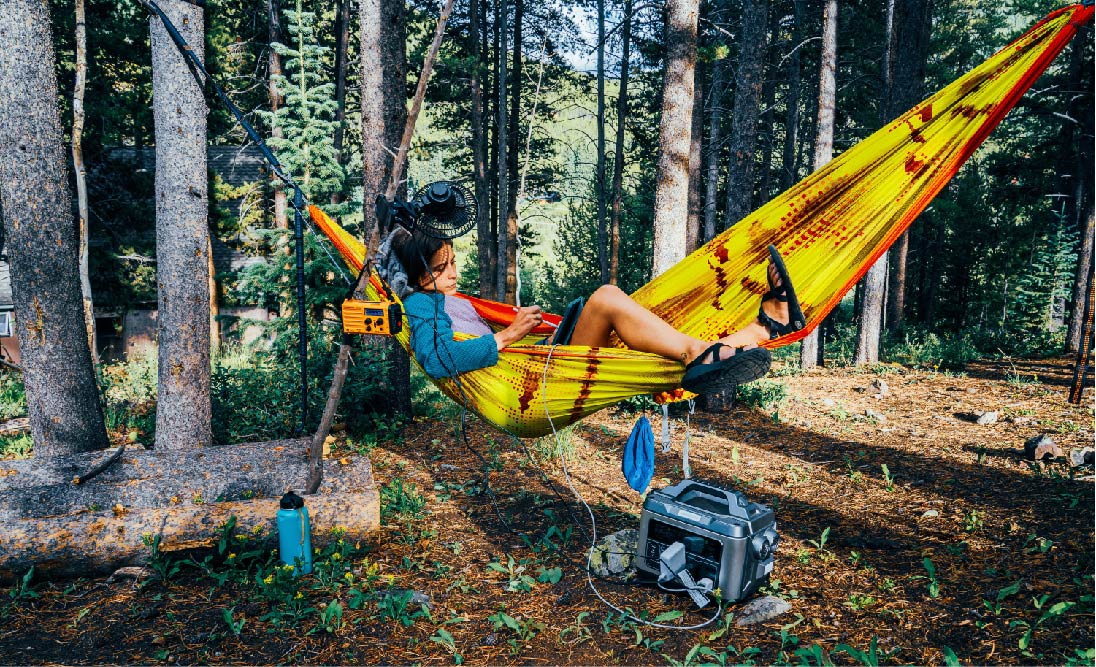
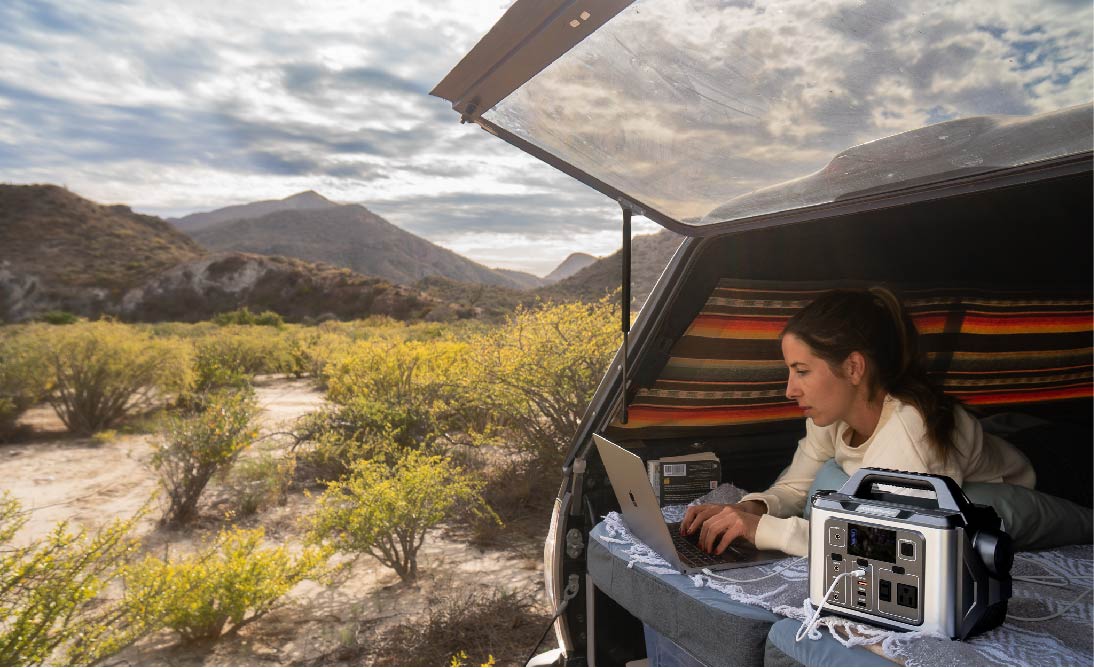
Camping and RV Trips: Solar generators provide portable and eco-friendly power for outdoor activities, charging devices, running camping equipment, and powering RV appliances.
-
Remote Work Sites: Solar generators are employed at remote work sites, such as construction or research locations, where access to the grid is limited, providing reliable power for tools and equipment.
-
Off-Grid Cabins: In off-grid cabins or cottages, solar generators supply sustainable power for lighting, heating, and running household appliances.
-
Emergency Preparedness: Solar generators serve as vital components of emergency preparedness kits, ensuring access to power for communication and essential devices during emergencies.
Wind Generators
-
Offshore Wind Farms: Large-scale wind generators are positioned offshore to harness strong winds for electricity generation, supplying power to coastal regions.
-
Rural Farming Operations: Wind generators are used in rural areas to power agricultural machinery, irrigation systems, and farm operations, reducing reliance on the grid.
-
Remote Weather Stations: Wind generators provide power to remote weather stations, ensuring uninterrupted data collection and communication in isolated regions.
-
Island Communities: Wind generators are utilized on islands where grid connections are limited, delivering a sustainable and consistent power supply to residents.
-
Eco-Tourism Resorts: Wind generators are incorporated into eco-tourism resorts, allowing visitors to experience sustainable and eco-friendly energy during their stay.
Fuel-Powered Generators with Battery Storage
-
Emergency Backup Power: These generators with battery storage serve as crucial backup power sources for homes, businesses, and critical infrastructure during power outages.
-
Construction Sites: Fuel-powered generators with battery storage are deployed at construction sites to provide electricity for power tools, lighting, and site operations.
-
Remote Telecommunications Towers: They ensure continuous power supply for remote telecommunications towers, preventing disruptions in mobile network coverage.
-
Outdoor Events: These generators are used to power outdoor events, concerts, and festivals, where a reliable power source is essential for stage equipment and lighting.
-
Medical Facilities: Hospitals and clinics rely on them for emergency power backup to ensure uninterrupted patient care during blackouts.
Hybrid Generators
-
Island Microgrids: Hybrid generators are used to create microgrids on remote islands, integrating renewable energy sources with backup generators to achieve energy independence.
-
Mining Operations: Mining companies utilize hybrid generators to power their operations in remote areas, optimizing energy efficiency and minimizing environmental impact.
-
Military Bases: Military installations in remote locations employ hybrid generators to ensure a constant power supply for communication, surveillance, and operations.
-
Disaster Relief Camps: In disaster-stricken areas, hybrid generators are deployed to establish temporary relief camps, providing essential power for medical facilities and shelters.
-
Off-Grid Eco-Lodges: Eco-friendly lodges in remote natural reserves use hybrid generators to supply power for guests while minimizing the environmental footprint.
Home Energy Storage Systems
-
Residential Solar Integration: Home energy storage systems are integrated with residential solar panels, storing excess solar energy for use during the night or on cloudy days.
-
Load Shifting: These systems are used for load shifting, charging during off-peak hours when electricity rates are lower, and discharging during peak demand to save on energy costs.
-
Grid Support: They provide grid support by injecting stored energy during periods of high demand, stabilizing the grid, and reducing strain on power infrastructure.
-
Electric Vehicle Charging: Home energy storage systems can charge electric vehicles, promoting sustainable transportation and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
-
Resilience During Grid Failures: In areas prone to power outages, these systems offer resilience by providing backup power for critical home appliances and medical equipment.
Why Choosing a Rechargeable Generator Over a Traditional Generator

Rechargeable generators, powered by renewable resources like solar and wind, offer a significant advantage over traditional generators. Their reliance on clean energy sources is just the tip of the iceberg. These generators come with a host of other advantages that make them an attractive choice for a wide range of applications. Let's explore some of these key benefits in more detail.
-
Sustainability and Renewable Energy Sources: Solar generators, being a prime example of rechargeable generators, harness the power of renewable energy sources, specifically sunlight. This sustainability reduces greenhouse gas emissions, contributes to a cleaner environment, and supports the global transition to clean energy.
-
Quiet Operation and Reduced Noise Pollution: One distinct advantage of rechargeable generators, particularly solar generators, is their remarkably quiet operation. The absence of noisy internal combustion engines makes them suitable for both urban and rural environments, minimizing noise pollution. This quietness is particularly appreciated in residential areas and during outdoor events where tranquility is valued.
-
Low Operating Costs and Cost Savings: Solar generators stand out for their low operating costs. They utilize abundant and free sunlight, requiring minimal maintenance. Once the initial investment is made in solar panels and a rechargeable battery, the ongoing operational expenses are significantly lower compared to traditional generators powered by fuel. This translates to cost savings in the long run and is an attractive feature for both residential and commercial applications.
-
Environmental Friendliness and Reduced Ecological Footprint: Rechargeable generators, with solar generators as a prime example, have a smaller ecological footprint. By utilizing renewable energy and minimizing reliance on non-renewable fuels, they play a crucial role in conserving the environment. This is especially relevant in the context of combating climate change and protecting natural habitats.
-
Energy Independence and Grid Resilience: Solar generators provide an impressive degree of energy independence. By generating your power from sunlight, you reduce your reliance on the grid. This offers resilience during power outages or grid failures, ensuring that essential appliances and devices remain functional. It's an important feature for homeowners, especially in regions prone to blackouts.
-
Portability and Versatility: Many rechargeable generators, including solar generators, are designed with portability in mind. This feature is highly advantageous for outdoor enthusiasts, campers, and off-grid adventurers. Solar generators are lightweight, easy to transport, and can provide clean energy wherever the sun shines. This versatility expands their utility to a wide range of activities and remote locations.
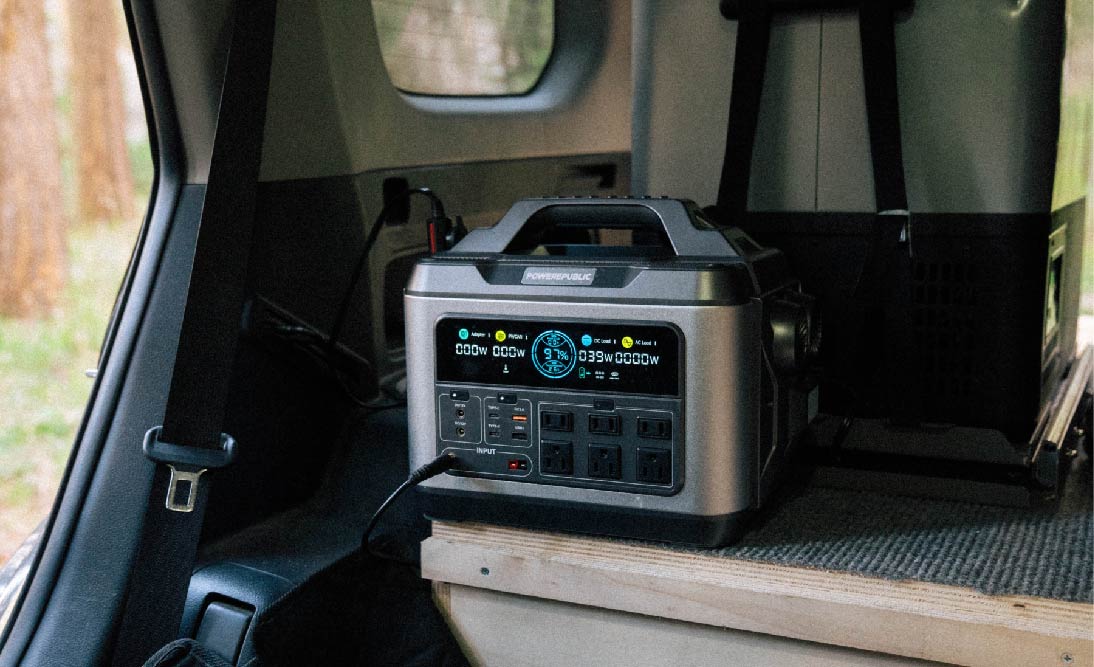
POWEREPUBLIC Solar Generator Kits as Rechargeable Generators

POWEREPUBLIC provides portable power solutions for off-grid living. Among our various models, we highly recommend the T306 and T1200 solar generator kits due to their exceptional portability, versatility, and functionality.
The table below presents essential information about our T306 and T1200 models:
|
Model |
Specs |
Recharge Time |
|
Power Output: 300W, Surge 600W Battery Capacity: 296Wh Battery Type: Lithium-ion with 800+ cycles to 80% Weight: 9.2Ibs/4Kg Dimension: 11.2*6.1*8.0 inch Output: 10 output ports Solar Input: 120W Max. |
AC: 3 - 4 hours Car Socket(12V/8A): 3- 4 hours |
|
|
Power Output: 1200W, Surge 2600W Battery Capacity: 1110Wh Battery Type: Lithium-ion with 800+ cycles to 80% Weight: 31Ibs/14Kg Dimension: 14.3*9.3*10.6 Inch Output: 13 output ports Solar Input: 220W Max. |
AC: 4 - 5 hours Solar(200W): 5- 6 hours Car Socket(12V/8A): 9 -10 hours |
Please note that: Solar input can vary based on weather conditions, and vehicle car sockets may have different voltage and current requirements.
Final Thoughts
In summary, as the world becomes more concerned about taking care of the environment, rechargeable generators are becoming a popular choice. These generators can provide backup power using clean, renewable sources like solar and wind energy, and they have many benefits. They come in different types, such as solar and wind generators, hybrid models, and home energy storage systems. Each type stores energy in batteries, charges using specific sources, and keeps recharging to make sure you have power when you need it.
Choosing a rechargeable generator over a traditional one is a great idea. They use clean energy, are quiet, and cost less to run. They're also better for the environment and can keep your lights on during power outages. Plus, they're easy to take with you wherever you go.
POWEREPUBLIC offers two excellent models, the T306 and T1200, for portable power. These solar generator kits are perfect for off-grid living, and you can see their specifications in the table above. So, when you're thinking about power solutions, consider rechargeable generators for a cleaner, more reliable energy source.